For my own personal use only:
- Metabolic bone disease
(MBD)
- Classic case:
- "Bent iguana" (pathologic fractures) OR
- Progressive weakness in a young reptile OR
- Swollen limbs from fibrous osteodystrophy
- History of a deficient diet (unsupplemented lettuce, ground meat, mealworms, crickets)
- Dx:
- Physical exam: distorted, rubbery mandible
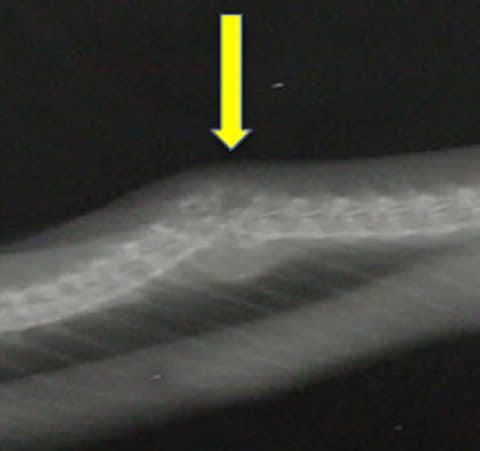
- Radiography: poor mineralization, greenstick fractures
- Low plasma 25-dihydroxycholecalciferol
- Later see hyperphosphatemia and hypocalcemia
- Tx:
- CRITICAL: Correct diet and lighting
- Dietary Ca:P = 1.5-2.1
- Unfiltered sunlight or full spectrum light (UVB) needed for vitamin D3
- "Gut-load" whole prey (prey supplemented with calcium or calcium/vit D)
- Calcitonin: only if normocalcemic
- CRITICAL: Correct diet and lighting
- Pearls:
- Prognosis is fair to good if caught early, but poor if hypocalcemia and bone loss
- Renal secondary hyperparathyroidism can occur in older
animals with end-stage renal disease
- Present with inability to move and muscle fasciculations
- Classic case:
- Salmonellosis
- Classic case:
- Reptiles AND amphibians are often carriers, shedding bacteria in feces
- May see septicemia, osteomyelitis, abscesses
- Dx:
- Culture (abscess or blood)
- Biopsies
- Radiographs: vertebral infection in snakes
- Necropsy: acute enteritis or necrotizing fibrinous enteritis
- Tx:
- Debridement
- Systemic antibiotics if septicemic (may increase emergence of resistant strains)
- Supportive care
- Fluids
- NSAIDs
- Pearls: ZOONOTIC concern
- Red-eared slider turtles illegal to sell if under 4 inches of shell length (can fit in child's mouth)
- Practice good hygiene after handling reptiles or amphibians, enclosures, and their food
- Children under 5, the elderly, and people with compromised immune systems are at high risk of infection
- Etiology: Usually S. bongori or S. enterica
- Classic case:
- Dysecdysis (retained shed)
- Classic case:
- Snakes with retained or partially shed skin
- Lizards: see over feet and toes, can constrict distal toes and tail tip
- Dx:
- Physical exam
- Rule out underlying disease
- Tx:
- Soak animal prior to assisting shed
- Be careful with retained spectacles, can damage cornea
- Treat underlying disease
- Pearls:
- Environment may be too dry or poor nutrition
- Subspectacular abscesses can occur between cornea and spectacle
- Exuvium is the shedded whole skin (snakes)
- Lizards shed in pieces
- Classic case:
- Gout
- Classic case:
- Visceral: obtunded, weak, dehydrated
- Primary is caused by excess dietary protein
- Secondary is due to dehydration or renal disease
- Articular: swellings, white nodular tophi (urate-centered granulomas) around appendicular joints, PAINFUL
- Rare to have both types in one animal
- Visceral: obtunded, weak, dehydrated
- Dx:
- Increased blood uric acid levels
- Radiographs show mineralized tophi in organs or joints
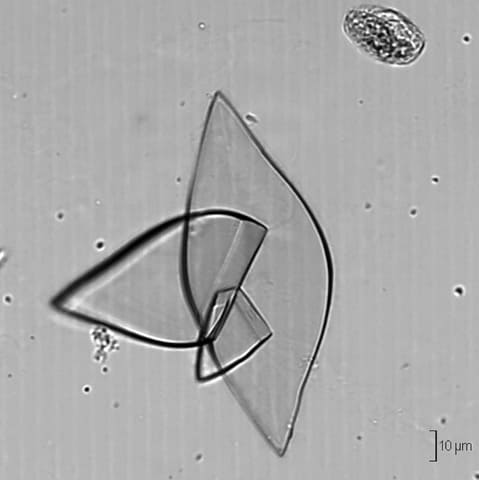
- FNA of joints: see needle-shaped crystals
- Tx:
- Rehydration/abundant access to water, vitamin supplementation, analgesics
- Primary visceral: decrease dietary protein; try to approximate diet of reptile's natural habitat
- Secondary visceral: treat underlying disease
- Medical Rx is challenging, poorly understood & takes
cues
from human protocols
- Allopurinol, may decrease uric acid production (debated)
- Probenecid, to promote urate excretion
- Colchicine/corticosteroids to manage acute gouty arthritis attacks
- Pearls:
- Prognosis is poor
- Pseudogout occurs in turtles, with mineral deposition (not urate) in and around feet
- Classic case:
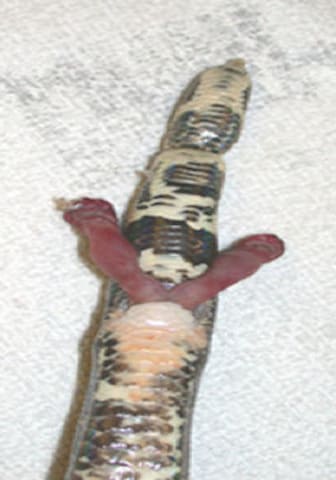
- Hemipenal and phallic
prolapse
- Classic case:
- Prolapsed structure, unable to retract
- Vulnerable to trauma during mating
- Dx: Physical exam
- Tx:
- Hypertonic topicals, lubricants, and reduction
- Surgical amputation: phallus and hemipenes have no urethra
- Pearls:
- Single phallus in crocodilians and chelonians
- Paired hemipenes in lizards and snakes
- Oviduct prolapse can occur in females when straining to pass eggs: SERIOUS
- Classic case:
Images courtesy of Jean A. Paré, DVM, DVSc, DACZM (MBD, snake spine, retained spectacles, prolapsed hemipenes), and Doruk Salanci (uric acid crystals).
Top Topic Category
Exotics