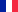
Key:
IM: Intramuscular
IV: Intravenous
SQ: Subcutaneous
- Always dose insulin based on (ideal) body weight, taking concurrent disease into consideration
- Combine insulin therapy with appropriate dietary management to optimize glycemic control
- Typically do not increase insulin dosage more frequently than every 1-2 wks
- Although manufacturer guidelines typically recommend discarding insulin after 4-6 wks, most insulin is efficacious if stored in the fridge for 3-6 mos; discard insulin that is discolored or has other changes in appearance
- Definition of diabetic control: Clinical signs of diabetes resolve; i.e., polyuria/polydipsia, weight loss, polyphagia; plus absence of hypoglycemia
Refs: Insulins commonly used in dogs and cats AAHA guidelines