For my own personal use only:
- Feline leukemia virus (FeLV)
- Classic case:
- Kitten or young adult, free-roaming, usually male
- "Ain't Doin' Right" (ADR)
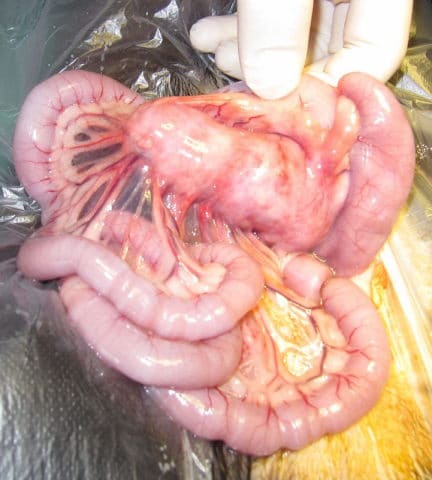
- +/- Abdominal or thoracic masses
- Dx:
- CBC: Leukopenia, neutropenia
- Radiography: Thorax and abdomen for FeLV-associated lymphosarcoma
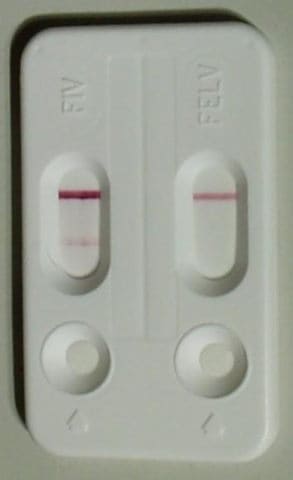
- Screen: Serum ELISA
- Confirmation: IFA
- Tx:
- Supportive: Antibiotics, nutritional support, fluids
- Stress-free environment
- Separate from FeLV-negative cats
- Pearls:
- Prognosis: Fair to poor
- Transmission: Saliva exchange
- Vaccinate kittens against FeLV; continue vaccinations if high risk
- IFA-positive cats persistently infected for life
- Classic case:
- Feline immunodeficiency virus
(FIV)
- Classic case:

- Mature cat, usually intact male, lives outdoors, previous bite wounds
- Gingivitis, stomatitis
- ADR, fever, anorexia, lethargy
- Dx:
- CBC: Anemia, leukopenia (esp. neutropenia), thrombocytopenia
- Screen: Serum ELISA (false positive if vaccinated)
- Confirmation: Western blot (false positive if vaccinated)
- Tx:
- Supportive: Antibiotics, fluids, nutritional support
- Dental care
- Pearls:
- Prognosis: Good to excellent, most do well for years
- Some cats develop AIDS-like disease with profound neutropenia
- Test before FIV vaccination
- Classic case:
- Feline hyperthyroidism
- Classic case:
- Middle-aged or older cat
- Weight loss with increased appetite
- Vomiting, diarrhea
- Murmur, tachycardia, arrhythmia
- "Yowling" at night
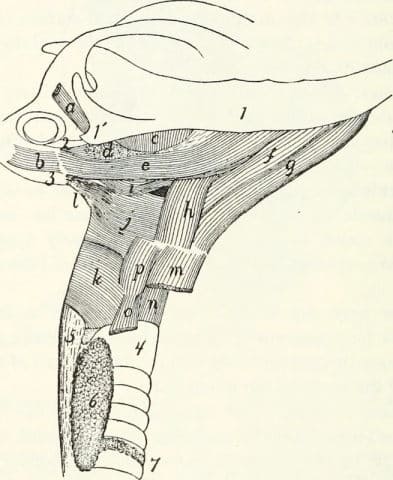
- Palpable thyroid nodules
- Dx:
- Screen: Total T4 (TT4) – may be high-normal with concurrent disease (euthyroid sick syndrome)
- Thyroid scintigraphy
- Echocardiogram and blood pressure
- Tx:
- Iodine 131 (I-131)
- Gold standard
- Most cases cured with ONE dose
- Anti-thyroid medication (methimazole, felimazole,
tapazole)
- Controls, but does not cure, many side effects
- Thyroidectomy: Risk of accidental parathyroid removal and life-threatening hypocalcemia
- Diet: Iodine restriction
- Iodine 131 (I-131)
- Pearls:
- Prognosis: Fair to excellent
- Adenomatous hyperplasia most common, neoplasia uncommon
- Less common presentation is "apathetic hyperthyroid": Anorexia, lethargy, etc.
- Click here to see a thyroid nodule in a cat from the Merck Vet Manual
- Classic case:
- Hepatic lipidosis
- Classic case:
- Obese cat with several-day history of anorexia
- Weight loss, jaundice
- Ptyalism when hepatic encephalopathy (HE) present
- Dx:
- Serum biochemistry: ALP higher than ALT, total bilirubin increased, normal GGT (helps differentiate from other hepatobiliary diseases)
- Coagulopathies
- Abdominal ultrasound
- Liver fine-needle aspirate (FNA) or biopsy
- Tx:
- Nutritional support is key
- Esophagostomy tube
- High-quality, high-protein diet (unless HE present)
- Avoid glucocorticoids
- If HE: Lactulose retention enemas
- Nutritional support is key
- Pearls:
- Prognosis: Fair to excellent
- Treat hyporexic and anorexic cats promptly and aggressively
- Classic case:
- Chronic renal disease
- Classic case:

- Senior or geriatric cat
- Polyuria and polydipsia
- Weight loss, vomiting
- Lethargy, hyporexia/anorexia
- Small, lumpy, bumpy kidneys
- Dx:
- Azotemia and hyperphosphatemia
- +/- Hypokalemia and anemia
- Dilute or isosthenuric urine
- High blood pressure
- Urine protein:creatinine ratio > 0.4
- Abdominal ultrasonography
- Tx:
- Supportive care: Appetite stimulants, anti-emetics, H2-blockers, fluids, K+ supplements, anti-hypertensive medication, phosphorus binders
- Nutrition: Renal prescription diets
- Pearls:
- Prognosis: Poor to good, depending on severity and concurrent illnesses
- Classic case:
Images courtesy of Stephanb (queen with litter), Dr. Uwe Gille (mesenteric lymphosarcoma, subcutaneous fluids), Kalumet (FIV/FeLV ELISA), Anatomy of the Cat (thyroid anatomy), AGarren (cat with feeding tube), and Art man (cat nose).
Top Topic Category
Feline